Path Too Long Auto Fixer v4.9 is the 1st tool that discovers, reports and auto corrects filenames and paths that are too long to fit under the MAXPATH 260 character limit in bulk.
Be sure all your back-up files are copied. Other tools make you go through hundreds of files, one-by-one, renaming and copying them somewhere. Who has time for that now-avoidable activity? Save a huge amount of an IT administrators time to correct this.
The most common way to get the path too long error is to have a too many sub-directories. For example the path below has 20 sub-directories! This is known a as deep directory and is very common in many work place shared drives, downloads and files shared on other operating systems (Max\Linux). The other common way is a filename is just too long.
Coping this path in Windows Explorer will fail.
Path Too Long Auto Fixer automatically fixes hundreds of deep directories and filenames so you don't have to .
Now you can copy and sync your hundreds of files to the cloud, with out error.
Don't miss a file, on your USB backups or to the cloud.
Never miss an Online Backup again

OneDrive, GDrive and Dropbox, etc all enforce the the 260 character limit. You may not even see the errors if you don't check the logs, which most users do not.
File Server Migration Mitigation
 Request Demo Download v4.0, not v4.9
Request Demo Download v4.0, not v4.9
PathTooLongAutoFixerR4DEMO.zip - You have to answer a few security questions to get demo. Send me your LinkedIn profile for faster processing and validate you are a real person.
Unzip and double-click PathTooLongAutoR4DEMO.exe*
* Limited to return 2 rows and opens this blog page.
Guaranteed no malware, no spyware, no evil-ware of any sort, like the rest of my tools.
But I do like to get paid. Free demo tool.
Path Too Long Auto Fixer uses a patent pending unique algorithm that shortens paths and filenames. It working its way back up the directories levels, shortening up, until the length is legal. This process is consistent for successive runs. Shortened paths are still readable and easily identifiable from the source.
This is a non-destructive process. No files will be lost. This is a copy, not a move or delete process. Until you are ready. There is an new option to delete long source file paths, and fix this issue for good, or at least until your next period of review.
PTLAF does what no other tool can;
Path Too Long Auto Fixer (PTLAF) rocks because in a few steps you can copy thousands of files . PTLAF will identified the multitude of long paths (directories) and filenames and correct them so you manually do not have too!
PTLAF is the first and only tool on the market that does this today !
PTLAF use an innovative algorithm to shortening filenames and paths so they are still human readable and unique. We are not using 8.3 names here, we have designed our own algorithm here. Download and try it for free!
Release R4 Client App
Path Too Long Auto Fixer rocks because can copy thousands of files to a new directory in seconds.

A quick 4 step process;
Note C will include empty directories that are too long.
Note E advance menu, including Advanced Options, Help and About.
Using Advanced Options Window Tips
Quick Tips;

When you click Generate Script button this will generate a Powershell Script to copy shortened paths. The script will open in Powershell ISE.
Prerequisites;
2 Step Process;
Step 1 - Follow steps in Quick Instructions - One Button Fix tab, but choose run the Generated Script, instead of Fix button.
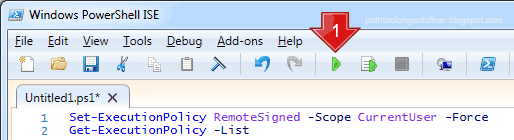
Step 2 - Just click the green arrow (as in step 1 in image below - red arrow) to run script.
If the Powerswhell ISE, does not open check %userprofile%\Documents check for most recently created script. Generated scripts have the following naming convention FixLongPaths_{TIMESTAMP}.ps1.
You can review the script if you like, and change file names.
Done.
Typical Issues;
1) If script fails for some reason, you'll need to run this command if you are running Powershell script for 1st time.
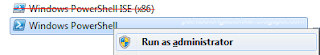
Search for "Windows Powershell", right-click and Run as Administrator (see image below).
and paste this command into it and press return.
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -Force - ExecutionPolicy Bypass
Close and run Powershell ISE as Administrator as well. Use file recent list to load last script and run.
2) Do you have . NET Framework 4 installed ? Check FAQ here. Or use this tool available here.
Licensing
For license inquires send email via contact form (right panel).
Licenses are sold on a per seat basis, tied to user account and hardware fingerprint.
This documentation is a work in progress while final version is being developed.
C:\> PTLAutoFix.exe -h for this help
Help/Usage: PTLAutoFix.exe Root="C:\Users\Golden Eye\Documents" [Dest="C:\User\Golden Eye\Onedrive"] [Min=250] [Delim=ALL] [Output=All] [pfl=0] [wf=true] [tc=1] [fc=1] [c=1] [et=1], [] indicates optional args, case insensitive
-- required --
Root="drive:\path"
The root directory path(quoted) to start recursively enumerating all sub-directories and files.
-- optional --
Dest=["drive:\path"]
The destination path(quoted) to replace the Root directory in the results. Default is null.
Search=[searchstring]
A file search pattern to filter filenames with. '*' matches many, '?' matches a character. Repeating '?' is supported, ie '*.???'. Searching for '*.' (no extension) is supported. Default is '*'.
Min=[0-32767]
An integer indicating the minimum length that a path must contain in order to be returned in the results. Default is 260.
Max=[0-32767]
An integer indicating the maximum length that a path may have in order to be returned in the results. Default is 32767.
Format=[Len|Path|Both|SLen|SPath|SBoth|Paths|All]
Format the resultant output. To display the [Len]gth or [Path], or [Both](combined) of found paths. Likewise, for the shortened length [SLen] or path [SPath], or both combined [SBoth] of the found shortened paths. [Paths] = Path + Spath. Default is All.
Delim=[S|H|U|HS|US|All3HSU|P|SP|HP|UP|HSP|USP|ALL|NONE]
Specifies a delimiter used to split each sub-dir path into words. Delimiters are combinations of Unicode Spaces(S), Hyphens/Dashes(H), Underscores(U) and Punctuation(P) characters. Note: Using NONE will preserve src path (loosely mimicking a normal copy cmd), BUT will truncate paths to 260 characters long, to be valid. Default is All3HSU, removing Hyphens, Spaces and Underscores.
Sort=[Asc|Dsc]
Indicates sort order of the returned results. Default is Dsc (Descending).
Copy=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to copy source files to shortened target. Default is 0 or false. ATTENTION: Full collision detection correction is auto set "fc=1" to true.
dsf=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to delete all source files, use "ed" for directories. Must be used simultaneously with the "Copy" argument. Default is 0 or false.
ed=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to add empty directories in the results. If used in conjunction with the "dsf" argument, it will delete source empty directories. Default is 1 or true.
ded=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to post detect and delete all empty directories possibly surfaced by using "dsf" argument. "copy", "dsf" and "ed" arguments must be simultaneously specified. Default is 0 or false.
mft=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to tag media files in the output. Default is 1 or true. Media files types scanned are *.mp?|*.m4?|aiff|*.au|*.aup|*.epub|*.ipa|*.itc2|*.itl|*.itdb|*.m3u|*.m3u8|*.mid|*.mov|*.mpg|*.pls|*.wav|*.wma|*.wmdb|*.wpl|*.xspf. Default is 0 or false.
mfw=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to enable media files warning and immediately stop processing if a media file is found, especially during a copy. Default is 1 or true.
pfl=[0-257]
An integer indicating the filename length (NOT including file extension length) for which shortening process will be overlooked. This enables preserving the name for 'smaller' filenames. This setting has no effect on shortening of sub-dirs. Default is 5
wf=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to use a blacklist word file (filterwords.csv, Unicode UTF-8 encoded) to remove words in each sub-dir path as split by Delim option. Replacement occurs for matching whole words only, not within a word. Order of words in the file is not important. Default is 0 or false.
gwf=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to use a global blacklist word file (globalfilterwords.csv, Unicode UTF-8 encoded) to remove words/characters in the entire path, a global search and replace. Replacement occurs within words. Order of words in the file is very important. Warning! Use wisely. Default is 0 or false.
tc=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to Title Case each word as split by delimiter option. Default is 0 or false.
fc=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to enable full collision detection correction. Default is 1 or true.
et=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the elapsed time to generate the resultant rows. Default is 0 or false.
c=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the count of number of resultant rows. Default is 0 or false.
l=[0-4294967295]
An unsigned integer indicating the number of lines to be returned in the results. Default is 0 (no limit).
lic=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the full license. Default is 0 or false.
v=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the current version. Default is 0 or false.
w=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the command line parsing warnings. Default is 1 or true, on for novices.
-h, a flag to output help.
Tested On:
Windows XP ,7, 8, 8.1, 10, 10 CU and equivalent Server releases
Optimal min. screen size XGA 1024 x 768 (4:3 aspect ratio, introduced in 1990)
Software Specifications:
Full Unicode support for filename and paths.
Shortcuts (.lnk) files are processed to keep file counts equivalent to Windows Explorer, but maybe invalidated if target directory has changed. This would occur in any tool including Windows itself, it's a perennial problem to manage shortcuts, but competitors never mention it. PTLAF provides a log file, to examine for affected files. Generally, this is an edge case (here for completeness) and not very common, since most users never use shortcuts.
To clear some ambiguity about Shortcuts created in Windows Explorer, they are listed as a 'file of type' "Shortcut (.lnk)" in Properties pop-up. They are not part of the symbolic link in classic NTFS reparse points definition. There are counted as files in PTLAF and Windows Explorer.
Junctions <JUNCTION>, directory symbolic links <SYMLINKD> and file symbolic <SYMLINK> which are part of the Windows NTFS reparse points are not processed PTLAF. These are types can be listed in DOS using DIR command and created using DOS MKLINK command. Windows Explorer correctly enumerates <SYMLINK> as a file. WARNING: Windows Explorer DOES NOT correctly enumerates <JUNCTION> or <SYMLINKD> links at all. It should be enumerated as a directory. Why do I mention this, so your understand the counts in PTLAF vs Windows Explorer.
A note about moving media files they have to potential to break media playlists, therefore are there's an option to tagged media files in log files. Offices files have same issue, because they can link to other files. Typically, Excel files can link to other Excel workbooks and if there references may break if moved or renamed. The log file can easily be searched for Excel files and Office files. Office files extensions are well known, and hence were not tagged separately in the log files. They can be individual searched for in the log file by their extension, ie .xlsx for Excel workbook.
Full Unicode support for path delimiters (dash, underscore, whites pace and punctuation) which are removed from the paths. Unicode vowels end with the Cyrillic code page. See Advanced Options Explained tab for more details.
Integrated AlphaFS 2.1 library to handle long paths over 260 characters and Unicode support. AlphaFS is a .NET library which is provided and supports extended length paths (longer than 260 characters).
Software Requirements:
Requires Microsoft .NET Framework 4 Framework. It's old but required for backwards comparability to Windows XP (and Windows Server 2003 ).
You can get .NET Framework 4.5 is a highly compatible, in-place update to .NET Framework 4. Download here .
Exception for Windows XP use
Microsoft .NET Framework 4 (Web Installer). Download here.
Do you have . NET Framework 4 installed ? Check FAQ here. Or use this tool available here.
Request Demo New Release 4 - Jan 1 2018

PathTooLongAutoFixerR4DEMO.zip - You have to answer a few security questions to get demo. Send me your LinkedIn profile for faster processing and validate you are a real person
Unzip and double-click PathTooLongAutoFixerR4DEMO.exe*
* Limited to return 2 rows and opens this blog page.
Guaranteed no malware, no spyware, no evil-ware of any sort, like the rest of my tools.
But I do like to get paid. Free demo tool.
Be sure all your back-up files are copied. Other tools make you go through hundreds of files, one-by-one, renaming and copying them somewhere. Who has time for that now-avoidable activity? Save a huge amount of an IT administrators time to correct this.
Coping this path in Windows Explorer will fail.
I:\WORK-CODE\EXAMPLE PATH TOO LONG\Documents\Business\Office Addon\v3-php-sdk-2.0.4\ v3-php-sdk-.0.4\Dependencies\XSD2PHP\test\data\expected\ContactCompany\oasis\names\ specification\ubl\schema\xsd\Common Aggregated Components\ system-maintained configuration file\Helpv1.1.docx
Path Too Long Auto Fixer automatically fixes hundreds of deep directories and filenames so you don't have to .
Now you can copy and sync your hundreds of files to the cloud, with out error.
Don't miss a file, on your USB backups or to the cloud.
Never miss an Online Backup again

OneDrive, GDrive and Dropbox, etc all enforce the the 260 character limit. You may not even see the errors if you don't check the logs, which most users do not.
File Server Migration Mitigation
With the imminent end of life support for Windows Server 2008, file server migrations maybe part of your upgrade plan to Windows Server 2019.
However, file server migrations with file names and paths that are too long will still fail. Moreover, the Storage Migration Service will fail to the Azure cloud.
And note, the new Windows 2019/Windows 10 Path Too Long setting is not fully integrated into the entire system, so CMD.exe and Windows Explorer will not copy paths that are too long.
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/jeremykuhne/2016/07/30/net-4-6-2-and-long-paths-on-windows-10/
However, file server migrations with file names and paths that are too long will still fail. Moreover, the Storage Migration Service will fail to the Azure cloud.
And note, the new Windows 2019/Windows 10 Path Too Long setting is not fully integrated into the entire system, so CMD.exe and Windows Explorer will not copy paths that are too long.
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/jeremykuhne/2016/07/30/net-4-6-2-and-long-paths-on-windows-10/
PathTooLongAutoFixerR4DEMO.zip - You have to answer a few security questions to get demo. Send me your LinkedIn profile for faster processing and validate you are a real person.
Unzip and double-click PathTooLongAutoR4DEMO.exe*
* Limited to return 2 rows and opens this blog page.
Guaranteed no malware, no spyware, no evil-ware of any sort, like the rest of my tools.
But I do like to get paid. Free demo tool.
What is the Path Too Long Error?
When a path such as "C:\directoryA\filenameB.txt" which consists of a directory (A), filename (B, including extension) and drive letter (C) is great than 260 characters in length you will get the path too long error when coping/deleting/altering or moving.
It must meet this criterion;
A (directory length) + B (filename length) + C <= 260 characters
This Windows API MAX_PATH constant sets the max length to 260, and is used to build Windows Explorer. So when you use Windows Explorer to copy invalid lengths it fails.
This limit was imposed for a backwards compatibility issue with older Windows versions. FAT32, and NTFS has supported long path names (up to ~32768 characters), and many times programs could get around this length. Especially, other files systems such as MacOS/Linux where there is not limit to number sub-directories (each sub-dir with a max of 247 characters). So coping files from those OSes via a mounted/USB drive will fail.
Using Windows Explorer and .NET programs (this includes Powershell too) will give you this error.
It must meet this criterion;
A (directory length) + B (filename length) + C <= 260 characters
- A. The filename with extension (filename.txt) must be less than or equal to 256 characters. (260-3-1)=256. Less 3 characters for drive letter C and 1 is for the invisible terminating null character.
- B. The directory name must be less than or equal to 247 characters.
(260-9-3-1) = 247. Less a minimum filename (including the extension) of length 9 to be created, drive letter C, and the invisible terminating null character. - C. The drive letter with a : colon and backslash \ characters for length of 3 characters max.
- Combined A+B+C must be less than or equal to 260 characters.
This Windows API MAX_PATH constant sets the max length to 260, and is used to build Windows Explorer. So when you use Windows Explorer to copy invalid lengths it fails.
This limit was imposed for a backwards compatibility issue with older Windows versions. FAT32, and NTFS has supported long path names (up to ~32768 characters), and many times programs could get around this length. Especially, other files systems such as MacOS/Linux where there is not limit to number sub-directories (each sub-dir with a max of 247 characters). So coping files from those OSes via a mounted/USB drive will fail.
Using Windows Explorer and .NET programs (this includes Powershell too) will give you this error.
Common Path Too Long Errors
A list of most common “File Name Too Long Errors” messages below;
The most frequent errors are;
Other errors that are not so obvious but are caused by Path Too Long error;
The most frequent errors are;
- Source Path Too Long - The source filename(s) are larger than is supported by the filesystem.
- Destination Path Too Long - The filename(s) would be too long for the destination folder.
- Interrupted Action - An unexpected error is keeping your from coping the file.
Error 0x80010135: Path Too Long - Delete Folder - An unexpected error is keeping you from deleting the folder.Error 0x80070003: The system cannot find the path specified.
- Error 1320: The specified path is too long.
- The file name you specified is not valid or too long. Specify a different file name.
Other errors that are not so obvious but are caused by Path Too Long error;
- Cannot delete file: access is denied
- There has been a sharing violation.
- The source or destination file may be in use.
- The file is in use by another program or user.
- Make sure the disk is not full or write-protected and that the file is not currently in use.
- Error Deleting File or Folder
- Error Copying File or Folder
- Cannot delete file or folder
- Cannot Open
- Cannot Copy
- The file could not be accessed
- File name could not be found
- Could not find this item
Competition Breakdown
The heavily advertised Path Too Long Software and Path Too Long tool which is same company can only copy long paths to shorter paths.
These tools are just copy tools, not discovery tools. My tool discovers and fixes paths that are tool long. Its specially purpose built for that in mind, to help a novice or an administrator to get the job done.
Gotcha! These tools don't mention you have painstaking manually copy each long directory to a new shorter directory. Where are they ? How many are there ?
Usually, there are huge number files fanned out to many different directories, particularly on shared drives at work. Currently, hard drives have a capacity of 12Tb of space or approx. 3,115,264 office documents!
Competitor tools make you have to select either directories or files one-by-one and copy it somewhere. Will it work? You are guesstimating that new directory length is short enough. What if it not? Repeat, and try again. What if the filename is still too long?
Who has the time to rename and move 100+ files to new directories?
Issues with competitor tools;
1) They do find the paths tool long to begin with!
2) You have to move/rename each directory or filenames one-by-one
3) They don't find filenames that are too long, so moving will not help
4) No algorithm to specifically fix long paths
4) No automation to fix long paths
Both FastCopy, Path Tool Long tool and others do not identify filenames that are too long to begin with.
These tools make you have to rename each filename one-by-one, if you elect to do so. If you don't next time you copy these files, you get the error. It's an incomplete solution. I am repeating myself because its seems people continue to buy those tools, without understanding the issue.
Path Too Long Auto Fixer is only tool that automatically finds and fixes long paths and filenames on the market today!
These tools are just copy tools, not discovery tools. My tool discovers and fixes paths that are tool long. Its specially purpose built for that in mind, to help a novice or an administrator to get the job done.
Gotcha! These tools don't mention you have painstaking manually copy each long directory to a new shorter directory. Where are they ? How many are there ?
Usually, there are huge number files fanned out to many different directories, particularly on shared drives at work. Currently, hard drives have a capacity of 12Tb of space or approx. 3,115,264 office documents!
Competitor tools make you have to select either directories or files one-by-one and copy it somewhere. Will it work? You are guesstimating that new directory length is short enough. What if it not? Repeat, and try again. What if the filename is still too long?
Who has the time to rename and move 100+ files to new directories?
Issues with competitor tools;
1) They do find the paths tool long to begin with!
2) You have to move/rename each directory or filenames one-by-one
3) They don't find filenames that are too long, so moving will not help
4) No algorithm to specifically fix long paths
4) No automation to fix long paths
Both FastCopy, Path Tool Long tool and others do not identify filenames that are too long to begin with.
These tools make you have to rename each filename one-by-one, if you elect to do so. If you don't next time you copy these files, you get the error. It's an incomplete solution. I am repeating myself because its seems people continue to buy those tools, without understanding the issue.
Path Too Long Auto Fixer is only tool that automatically finds and fixes long paths and filenames on the market today!
Why Path Too Long Auto Fixer ? What's the value add?
Path Too Long Auto Fixer uses a patent pending unique algorithm that shortens paths and filenames. It working its way back up the directories levels, shortening up, until the length is legal. This process is consistent for successive runs. Shortened paths are still readable and easily identifiable from the source.
This is a non-destructive process. No files will be lost. This is a copy, not a move or delete process. Until you are ready. There is an new option to delete long source file paths, and fix this issue for good, or at least until your next period of review.
PTLAF does what no other tool can;
- Identifies and fixes long paths in bulk.
- Choose how to shrink paths, remove space, underscores, punctuations or hyphens/dashes.
- Remove explicit words/characters from the paths.
- Identify media files, if moved, will break playlists.
- Command line for scriptability and automation
- Unicode control characters are removed from paths. All Unicode right-to-left characters (except U+061C in case you need this functionality) are removed. Right-to-left characters are used in malware attacks.
- Searching filenames with no extension "*." and matches repeating '?' is supported. For example, searching for all filenames with extension of length 3 is "*.???".
What make this solution the Best Choice ?
Path Too Long Auto Fixer (PTLAF) rocks because in a few steps you can copy thousands of files . PTLAF will identified the multitude of long paths (directories) and filenames and correct them so you manually do not have too!
PTLAF is the first and only tool on the market that does this today !
PTLAF use an innovative algorithm to shortening filenames and paths so they are still human readable and unique. We are not using 8.3 names here, we have designed our own algorithm here. Download and try it for free!
Release R4 Client App
Path Too Long Auto Fixer rocks because can copy thousands of files to a new directory in seconds.
Release V4.9 Improvements
- Added final fixed paths .CSV file
- Converted .TSV to .CSV files for Found Paths Grid Export
Release V4.8 Improvements
- Added adjustable setting Max Path Length [Range 16-260]
- Added adjustable sub-directory length [Range 1-247]
- Preserve File Name Hard Cut - just cut the filename, no shortening methods will be applied.
Release V4.6 Improvements
- Excel dump of found paths and compressed paths
- Tagging OneDrive files
- Better Unicode coverage for delimeter types
Release V4.5 Improvements
- One button FIX
- User interface is more responsive and user friendly (more warnings)
- Added new filename search filters such as searching files with no extension "*." and matches repeating '?' is supported. IE Search for extension of length 3 is "*.???"
- New delimiters. Delimiters are used to split each sub-dir path into words. Delimiters are combinations of Unicode Spaces, Hyphens/Dashes, Underscores and Punctuation characters.
- Added empty source directories detection and deletion option.
- Added media file detection in advanced options
- Collision detection, if generated shortened name happens to result in the same previous generated short name, this will rename it to avoid collisions.
- Fix button produces a full transaction log (C:\Users\{Username}\FixLongPaths_{timestamp}.log) so you can track file changes.
- Full Unicode support for paths and delimiters.
- Control characters are removed from paths. All Unicode right-to-left characters (except U+061C in case you need this functionality) are removed. Right-to-left characters are used in malware attacks.
Advanced Options Explained
1. Target MAX Path
3. Limit Results
4. PFL Hard Cut
5. Split Delimiter
All target paths will be shortened to this length. Default is 260. Range [16-260]2. Target Sub-Directory Length
Specify is an integer indicating sub-directory minimum length. This is the minimum each sub-directory will be shortened too. Default is 247 (Windows Directory Max). Range [1-247]
In extreme cases (for very very long paths > 300) , this setting maybe ignored.
3. Limit Results
Limit number of rows returned. Default is 0, for no limit, it returns ALL resultant rows.4. Preserve File Length (PFL)
Preserve file length (PFL) is intended to provide a sliding scale to the shortening length of the filename. This does NOT include extension length. For example, length 3, represents filesnames won.txt or won.text.
If you set to maximum of 257, then filename will not be shortened. To maximally shortened the filename you can set to 0 (this actually is just a convince, and represents a 1). Default is 5 characters long.In extreme cases (for very very long paths > 300) , this setting maybe ignored.
4. PFL Hard Cut
The filename will be chopped (from beginning of the filename, not including the extension) at PFL limit. No shorting will applied to chopped filename.
In extreme cases (for very very long paths > 300) , this setting maybe ignored.
5. Split Delimiter
Split Delimiter specifies a delimiter combination to split filename and sub-directories (if targeted for shorting) into words.
In the shortening process, all Unicode control characters** and vowels* are removed first, then specified delimiter is removed from the path, in order to shorten it.
There are 4 types of delimiters and are fully Unicode supported (meaning all characters found in the full range of Unicode characters are cataloged.)
Delimiters are Unicode white space (29 characters), Unicode underscores (11 characters), Unicode hyphens (38 characters) and Unicode punctuations (4,321) characters.
Punctuation delimiter represents all Unicode characters categorized as a punctuation. This consists of 567 punctuation characters including
!,",#,%,&,',*?,@,(,),[,],{,}... and 3,754 Unicode symbols including $,+,~,¢,£,¤,¥,¦,§, etc.).
*Note: There are 2,105 Unicode vowels that will be check against for each character in the path, if selected. All languages are included, except Chinese (any code point prefixed with CJK & Yi & Yijing). See https://unicode-table.com/en/blocks/.
**Note: A total of 84 Unicode Control characters and right-to-left characters are
removed. All Unicode right-to-left characters (except U+061C in case you need this functionality) are removed. You can use the blacklist word feature to remove U+061C Unicode characters as well. Right-to-left characters are used in malware attacks.
Default is All3HSU, and includes combintaion of hyphens(H), spaces(S) and underscores(U).6. Sort Order
Specifies sort order of the resultant rows and sort of order of copied rows to clipboard. Default is descending order.7. Tag Media Files?
Enabling this allows to optionally stop processing so you examine this issue in detail, before committing to changes. Media files that are moved/renamed will break playlists. This option will alert you and mark media files in generate script and log files, so you can track and communicate potential issues. Default is checked.
8. Title Case Path?Media files types scanned are *.mp?*.m4?aiff*.au*.aup*.epub*.ipa*.itc2*.itl*.itdb*.m3u*.m3u8*.mid*.mov*.mpg*.pls*.wav*.wma*.wmdb*.wpl*.xspf.
Specifies to title case each word in the path as split by Delimiter option (2 above). For example "justice league.txt" becomes "JstcLg.txt" using Space delimiter. Default is checked.9. Use Word Filter?
Blacklist word file (filterwords.csv, Unicode UTF-8 encoded) is used to remove words in each sub-dir path as split by Delimiter option (2 above). Replacement occurs for matching whole words only, not within a word. Order of words in the file is not important. Default is 0 or false.sort order of the resultant rows and sort of order of copied rows to clipboard. See Filtering Blacklisted Words from Paths tab for more information and file layout.10. Use Global?
Global blacklist word file (globalfilterwords.csv, Unicode UTF-8 encoded) is used to remove words/characters in the entire path, a global search and replace. Replacement occurs within words. Use wisely! Order of words in the file is very important. See Filtering Blacklisted Words from Paths tab for more information and file layout.11. Delete Source Files?
Delete all source files will fix long paths for good. Once you are comfortable with this tool
If not selected, clicking the Fix button, will prompt you 3 times to proceed with this. If selected, clicking the Fix button, the 3 times prompt will not appear.
Use wisely! Deleted files are not recoverable. There is no recycle bin.
Tip: Back-up your files beforehand. Use this tool periodically (monthly) to check your files. The command line can be scheduled to do this in a script.
Discovery Reports & Logs
Quick Instructions - One Click Fix

A quick 4 step process;
- Choose A Start Directory to search for long paths in.
Default will suffice in most cases, and points to user's document directory. - Choose B destination directory for files to Copy To. Can be external drive or cloud drive.
You can leave this blank and it will be an in-place copy. - Select 1 button to Find Paths Too Long.
Wait for results in D.
If there are no results, then you have no long paths!
Selecting rows and copy and paste into Notepad to examine rows in detail. - Select 2 Fix button to do process now.
Note C will include empty directories that are too long.
Note E advance menu, including Advanced Options, Help and About.
Using Advanced Options Window Tips
Quick Tips;
- Preserve File Length (PFL)
Choose 3 as absolute min to ensure filename and paths are still readable, but get maximal compression. But you can but can goto 0 if you really need to super crunch the file name. - Split Delimiter
Choose All for maximum removal of spurious characters like !@, in filename. - Word Filter - Comes pre-populated to check the file for values, so they work for you.
Filterwords.csv comes pre-loaded with some default words;
a, also, an, and, as, but, either, for, if, is, its, lest, neither, nor, or, so, such, than, that, the, their, these, this, those, yet
Quick Instructions - Generate Script (Powershell)

When you click Generate Script button this will generate a Powershell Script to copy shortened paths. The script will open in Powershell ISE.
Prerequisites;
- Requires Powershell_ISE and Powershell to use .NET 4.0 CLR. Check here.
- You can upgrade to Powershell 4.0 Windows Management Framework 4.0 download here.
- Do you have . NET Framework 4 installed ? Check FAQ here. Or use this tool available here.
2 Step Process;
Step 1 - Follow steps in Quick Instructions - One Button Fix tab, but choose run the Generated Script, instead of Fix button.
Step 2 - Just click the green arrow (as in step 1 in image below - red arrow) to run script.
If the Powerswhell ISE, does not open check %userprofile%\Documents check for most recently created script. Generated scripts have the following naming convention FixLongPaths_{TIMESTAMP}.ps1.
You can review the script if you like, and change file names.

Done.
Typical Issues;
1) If script fails for some reason, you'll need to run this command if you are running Powershell script for 1st time.
Search for "Windows Powershell", right-click and Run as Administrator (see image below).

and paste this command into it and press return.
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -Force - ExecutionPolicy Bypass
Close and run Powershell ISE as Administrator as well. Use file recent list to load last script and run.
2) Do you have . NET Framework 4 installed ? Check FAQ here. Or use this tool available here.
Licensing
For license inquires send email via contact form (right panel).
Licenses are sold on a per seat basis, tied to user account and hardware fingerprint.
- Home user license is $99.00 USD per computer.
- Business license is minimum charge of 3 seats (users) for a total of $257.00 USD.
Per seat cost for a small/large company or on a server is $97.00 USD. - VM License falls in Enterprise category.
- Enterprise (unlimited license, portable) please use contact form. Negotiable.
This documentation is a work in progress while final version is being developed.
Licensing Process
- I'll send you a License Info Gathering tool and email results back.
- This information is used to make a custom software build for you.

- Note: MAC address is used because it's a physical signature of your network card, and generally not supposed to be changeable, but easily is. Your MAC address will not be disclosed to anyone.
For added comfort read this;
"Is it safe to share you MAC Address ?" question on StackExhange . - Furthermore, all this information will not be share with anyone and is used exclusively for licensing of this product.
Extensive Scriptable Command Line for Administrators
C:\> PTLAutoFix.exe -h for this help
Help/Usage: PTLAutoFix.exe Root="C:\Users\Golden Eye\Documents" [Dest="C:\User\Golden Eye\Onedrive"] [Min=250] [Delim=ALL] [Output=All] [pfl=0] [wf=true] [tc=1] [fc=1] [c=1] [et=1], [] indicates optional args, case insensitive
-- required --
Root="drive:\path"
The root directory path(quoted) to start recursively enumerating all sub-directories and files.
-- optional --
Dest=["drive:\path"]
The destination path(quoted) to replace the Root directory in the results. Default is null.
Search=[searchstring]
A file search pattern to filter filenames with. '*' matches many, '?' matches a character. Repeating '?' is supported, ie '*.???'. Searching for '*.' (no extension) is supported. Default is '*'.
Min=[0-32767]
An integer indicating the minimum length that a path must contain in order to be returned in the results. Default is 260.
Max=[0-32767]
An integer indicating the maximum length that a path may have in order to be returned in the results. Default is 32767.
Format=[Len|Path|Both|SLen|SPath|SBoth|Paths|All]
Format the resultant output. To display the [Len]gth or [Path], or [Both](combined) of found paths. Likewise, for the shortened length [SLen] or path [SPath], or both combined [SBoth] of the found shortened paths. [Paths] = Path + Spath. Default is All.
Delim=[S|H|U|HS|US|All3HSU|P|SP|HP|UP|HSP|USP|ALL|NONE]
Specifies a delimiter used to split each sub-dir path into words. Delimiters are combinations of Unicode Spaces(S), Hyphens/Dashes(H), Underscores(U) and Punctuation(P) characters. Note: Using NONE will preserve src path (loosely mimicking a normal copy cmd), BUT will truncate paths to 260 characters long, to be valid. Default is All3HSU, removing Hyphens, Spaces and Underscores.
Sort=[Asc|Dsc]
Indicates sort order of the returned results. Default is Dsc (Descending).
Copy=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to copy source files to shortened target. Default is 0 or false. ATTENTION: Full collision detection correction is auto set "fc=1" to true.
dsf=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to delete all source files, use "ed" for directories. Must be used simultaneously with the "Copy" argument. Default is 0 or false.
ed=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to add empty directories in the results. If used in conjunction with the "dsf" argument, it will delete source empty directories. Default is 1 or true.
ded=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to post detect and delete all empty directories possibly surfaced by using "dsf" argument. "copy", "dsf" and "ed" arguments must be simultaneously specified. Default is 0 or false.
mft=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to tag media files in the output. Default is 1 or true. Media files types scanned are *.mp?|*.m4?|aiff|*.au|*.aup|*.epub|*.ipa|*.itc2|*.itl|*.itdb|*.m3u|*.m3u8|*.mid|*.mov|*.mpg|*.pls|*.wav|*.wma|*.wmdb|*.wpl|*.xspf. Default is 0 or false.
mfw=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to enable media files warning and immediately stop processing if a media file is found, especially during a copy. Default is 1 or true.
pfl=[0-257]
An integer indicating the filename length (NOT including file extension length) for which shortening process will be overlooked. This enables preserving the name for 'smaller' filenames. This setting has no effect on shortening of sub-dirs. Default is 5
wf=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to use a blacklist word file (filterwords.csv, Unicode UTF-8 encoded) to remove words in each sub-dir path as split by Delim option. Replacement occurs for matching whole words only, not within a word. Order of words in the file is not important. Default is 0 or false.
gwf=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to use a global blacklist word file (globalfilterwords.csv, Unicode UTF-8 encoded) to remove words/characters in the entire path, a global search and replace. Replacement occurs within words. Order of words in the file is very important. Warning! Use wisely. Default is 0 or false.
tc=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to Title Case each word as split by delimiter option. Default is 0 or false.
fc=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to enable full collision detection correction. Default is 1 or true.
et=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the elapsed time to generate the resultant rows. Default is 0 or false.
c=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the count of number of resultant rows. Default is 0 or false.
l=[0-4294967295]
An unsigned integer indicating the number of lines to be returned in the results. Default is 0 (no limit).
lic=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the full license. Default is 0 or false.
v=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the current version. Default is 0 or false.
w=[1|0] or [true|false]
A boolean to output the command line parsing warnings. Default is 1 or true, on for novices.
-h, a flag to output help.
Feature Highlight: Filtering Blacklisted Words from Paths
There are two way to remove words/characters from a path;
Most likely words you might like to remove are those you find redundant or non-descriptive. Your organization also may find and remove words that are verboten, like WTF and other internet slang. You can use this program to rename all you files (by doing a copy and delete, available in the generated script).
Saving a Unicode UTF-8 File:
If you plan to use Unicode characters in the .csv files make sure your are saving them as Unicode UTF-8 encoded file.
The file must not contain the following characters '<', '>', ':', '"', '/', '|', '?', '*' as they are reserved path and filename characters - see https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa365247.aspx for exact spec for valid path characters.
The words are case insensitive. If phrase includes spaces, double quote it.
Example blacklist file to remove the following words from path and filename:
҂, so, this, that, WTF, FML, IDGAF, "F*** You",TW*T
- You can use a blacklist word file (filterwords.csv, Unicode UTF-8 encoded) to remove words in each sub-directory path as split by Delimiter option. Replacement occurs for matching whole words only, not within a word. Order of words in the file is not important. Available in Advanced Options and command line.
Filterwords.csv comes pre-loaded with some default words;
a, also, an, and, as, but, either, for, if, is, its, lest, neither, nor, or, so, such, than, that, the, their, these, this, those, yet - You can use a global blacklist word file (globalfilterwords.csv, Unicode UTF-8 encoded) to remove words/characters in the entire path, a global search and replace. Replacement occurs within words. In other words, replacement occurs anywhere in the entire path. Order of words in the file is very important. Warning! Use wisely. Available in Advanced Options and command line.
Globalfilterwords.csv comes no pre-loaded with some default words.
Most likely words you might like to remove are those you find redundant or non-descriptive. Your organization also may find and remove words that are verboten, like WTF and other internet slang. You can use this program to rename all you files (by doing a copy and delete, available in the generated script).
- Remove internet slang - WTF, Dafuq = (What) the f***?, FML = F*** My Life, Bitch, IDGAF = I Dont Give A F***, etc.
- Remove conjunctions - for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so, as, if, either, neither, also, etc,
- Remove determinders - a, an, its, that, the, their, these, this, those, such, etc
- Remove a single letter - ҂,!,@,#,'
Saving a Unicode UTF-8 File:
If you plan to use Unicode characters in the .csv files make sure your are saving them as Unicode UTF-8 encoded file.
- Download and install this powerful free text editor: Notepad++
- Open the file you want to verify/fix in Notepad++
- In the top menu select Encoding > Convert to UTF-8 (option without BOM)
- Save the file
The file must not contain the following characters '<', '>', ':', '"', '/', '|', '?', '*' as they are reserved path and filename characters - see https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa365247.aspx for exact spec for valid path characters.
The words are case insensitive. If phrase includes spaces, double quote it.
Example blacklist file to remove the following words from path and filename:
҂, so, this, that, WTF, FML, IDGAF, "F*** You",TW*T
Technical Details
Tested On:
Windows XP ,7, 8, 8.1, 10, 10 CU and equivalent Server releases
Optimal min. screen size XGA 1024 x 768 (4:3 aspect ratio, introduced in 1990)
Software Specifications:
Full Unicode support for filename and paths.
Shortcuts (.lnk) files are processed to keep file counts equivalent to Windows Explorer, but maybe invalidated if target directory has changed. This would occur in any tool including Windows itself, it's a perennial problem to manage shortcuts, but competitors never mention it. PTLAF provides a log file, to examine for affected files. Generally, this is an edge case (here for completeness) and not very common, since most users never use shortcuts.
To clear some ambiguity about Shortcuts created in Windows Explorer, they are listed as a 'file of type' "Shortcut (.lnk)" in Properties pop-up. They are not part of the symbolic link in classic NTFS reparse points definition. There are counted as files in PTLAF and Windows Explorer.
Junctions <JUNCTION>, directory symbolic links <SYMLINKD> and file symbolic <SYMLINK> which are part of the Windows NTFS reparse points are not processed PTLAF. These are types can be listed in DOS using DIR command and created using DOS MKLINK command. Windows Explorer correctly enumerates <SYMLINK> as a file. WARNING: Windows Explorer DOES NOT correctly enumerates <JUNCTION> or <SYMLINKD> links at all. It should be enumerated as a directory. Why do I mention this, so your understand the counts in PTLAF vs Windows Explorer.
A note about moving media files they have to potential to break media playlists, therefore are there's an option to tagged media files in log files. Offices files have same issue, because they can link to other files. Typically, Excel files can link to other Excel workbooks and if there references may break if moved or renamed. The log file can easily be searched for Excel files and Office files. Office files extensions are well known, and hence were not tagged separately in the log files. They can be individual searched for in the log file by their extension, ie .xlsx for Excel workbook.
Full Unicode support for path delimiters (dash, underscore, whites pace and punctuation) which are removed from the paths. Unicode vowels end with the Cyrillic code page. See Advanced Options Explained tab for more details.
Integrated AlphaFS 2.1 library to handle long paths over 260 characters and Unicode support. AlphaFS is a .NET library which is provided and supports extended length paths (longer than 260 characters).
Software Requirements:
Requires Microsoft .NET Framework 4 Framework. It's old but required for backwards comparability to Windows XP (and Windows Server 2003 ).
You can get .NET Framework 4.5 is a highly compatible, in-place update to .NET Framework 4. Download here .
Exception for Windows XP use
Microsoft .NET Framework 4 (Web Installer). Download here.
Do you have . NET Framework 4 installed ? Check FAQ here. Or use this tool available here.
Request Demo New Release 4 - Jan 1 2018
PathTooLongAutoFixerR4DEMO.zip - You have to answer a few security questions to get demo. Send me your LinkedIn profile for faster processing and validate you are a real person
Unzip and double-click PathTooLongAutoFixerR4DEMO.exe*
* Limited to return 2 rows and opens this blog page.
Guaranteed no malware, no spyware, no evil-ware of any sort, like the rest of my tools.
But I do like to get paid. Free demo tool.
Software Requirements
Requires Microsoft .NET Framework 4 Client Profile now expired, but is accessible by
. NET Framework 4.5 is a highly compatible, in-place update to .NET Framework 4. Download here .
Exception for Windows XP use
Microsoft .NET Framework 4 (Web Installer). Download here.
Do you have . NET Framework 4 installed ? Check FAQ here. Or use this tool available here.
. NET Framework 4.5 is a highly compatible, in-place update to .NET Framework 4. Download here .
Exception for Windows XP use
Microsoft .NET Framework 4 (Web Installer). Download here.
Do you have . NET Framework 4 installed ? Check FAQ here. Or use this tool available here.
Satisfied Enterprise Customers
 |
| ACON Laboratories, Inc. in 130 countries |







No comments:
Post a Comment